Introduction:
In the dynamic landscape of virtualization, ensuring your Hyper-V virtual machines are running on the latest configuration version is vital for optimal performance and compatibility. In this detailed tutorial, we’ll delve into the reasons behind upgrading virtual machine configuration versions, the potential pitfalls of neglecting this process, and a step-by-step guide to seamlessly upgrade your virtual machines.
Within Microsoft Hyper-V, there exists a crucial component known as the VM configuration version, defining the configuration specifics, saved state, and snapshot capabilities of the virtual machine within the Hyper-V environment. Essentially, the VM configuration version serves as the architectural plan, outlining the features available to the virtual machine.
The general principle governing Hyper-V VM configuration versions is that modern Hyper-V hosts, equipped to support the latest VM configuration level, maintain compatibility with virtual machines configured for older VM configuration versions. However, the converse is not true – older Hyper-V hosts lack the ability to accommodate the new configuration versions.
In earlier iterations of Hyper-V, updating the Hyper-V software also automatically updated the virtual machine configuration version. However, with the advent of Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V, Microsoft introduced a departure from this automatic upgrade process. This shift brings forth distinct advantages compared to the previous automatic upgrades. It allows for increased flexibility in moving virtual machines between Hyper-V versions, catering to specific use cases prevalent in certain environments. Microsoft’s revised stance emphasizes a commitment to ensuring the backward compatibility of the VM configuration version, encompassing saved states and checkpoints.
Hyper-V administrators are strongly encouraged to proactively undertake the upgrade of the VM configuration version. This proactive approach ensures the utilization of the latest features available within Hyper-V virtual machines. By embracing this recommended practice, administrators can stay abreast of advancements, optimizing the performance and capabilities of their virtualized environments.
How to Identify a Virtual Machine Configuration Version ?
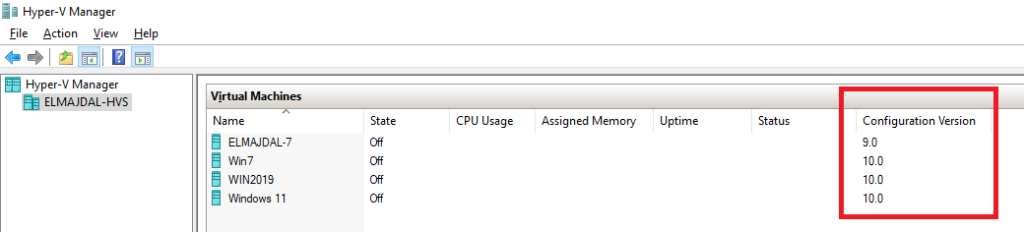
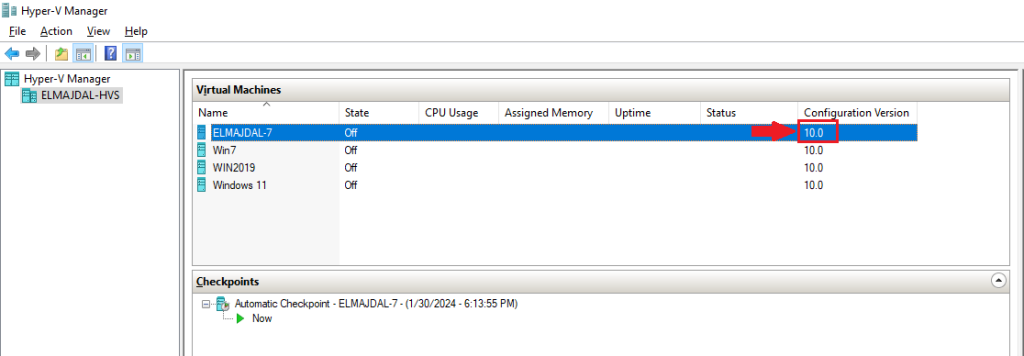
- The configuration version is displayed inside the Hyper-V Manager console beside the name of each virtual machine as seen in the below screenshot.

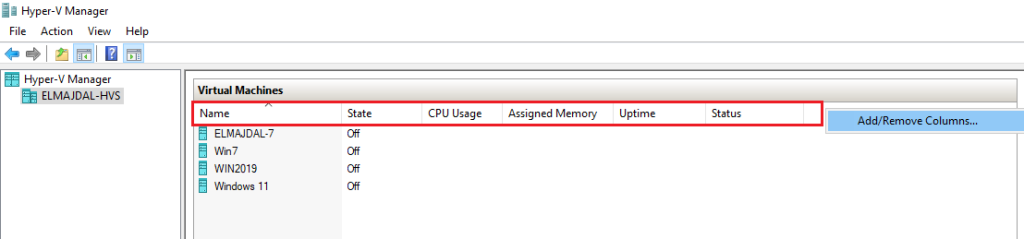
- If the Configuration Version column is not available/displayed, you can simply add it by right clicking on any of the column names, and then click Add/Remove Columns…

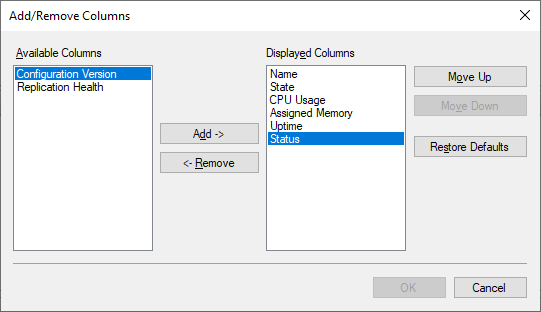
- The Add/Remove Columns page will open, select the Configuration Version from the left side > Click Add and then click OK

- You can also check the configuration version of the selected Virtual machine from the Summary tab at the bottom of Hyper-V Manager

The following table shows a full list of VM configuration versions of Hyper-V VMs together with the operating system.
| Windows Client | Windows Server | Version |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 | 1.0 | |
| Windows Server 2008 SP1 | 2.0 | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 3.0 | |
| Windows 8 | Windows Server 2012 | 4.0 |
| Windows 8.1 | Windows Server 2012 R2 | 5.0 |
| Windows 10 1507 | Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 3 | 6.2 |
| Windows 10 1511 | Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 4 | 7.0 |
| Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 5 | 7.1 | |
| Windows 10 Anniversary Update | Windows Server 2016 | 8.0 |
| Windows 10 Creators Update | 8.1 | |
| Windows 10 Fall Creators Update | Server 1709 | 8.2 |
| Windows 10 April 2018 Update | Server 1803 | 8.3 |
| Windows 10 October 2018 Update | Windows Server 2019 / 1809 | 9.0 |
| Windows 10 May 2019 Update | Server 1903 | 9.1 |
| Windows 10 May 2020 Update | Server 2003 | 9.2 |
| Windows 10 May 2021 Update | 9.3 | |
| Windows 11 | Windows Server 2022 | 10.0 |
What Happens if You Don’t Upgrade?
Failure to upgrade the virtual machine configuration version may lead to incompatibility with features available on the newer host OS. To unlock these advanced features, it’s highly recommended to update the configuration version once you’ve successfully upgraded the virtualization hosts to a newer Windows version.
The following table shows the minimum virtual machine configuration version required to use some Hyper-V features.
| Feature | Minimum VM configuration version |
|---|---|
| Allow additional processor features for Perfmon | 9.0 |
| Automatically expose simultaneous multithreading configuration for VMs running on hosts using the Core Scheduler | 9.0 |
| Hibernation support | 9.0 |
| Increase the default maximum number for virtual devices to 64 per device (e.g. networking and assigned devices) | 8.3 |
| Guest Virtualization-Based Security support (VBS) | 8.0 |
| Key storage drive | 8.0 |
| Large memory VMs | 8.0 |
| Nested Virtualization | 8.0 |
| Virtual processor count | 8.0 |
| XSAVE support | 8.0 |
| Virtual Machine Multi Queues (VMMQ) | 7.1 |
| Virtual Trusted Platform Module (vTPM) | 7.0 |
| Hot Add/Remove Memory | 6.2 |
| PowerShell Direct | 6.2 |
| Production Checkpoints | 6.2 |
| Secure Boot for Linux VMs | 6.2 |
| Virtual Machine Grouping | 6.2 |
Upgrading Virtual Machine Configuration Version
To upgrade a Virtual Machine Configuration Version, follow the below steps:
- Shutdown the Virtual Machine
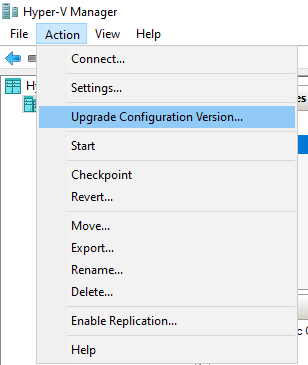
- Select the Virtual Machine and then from the menu bar, click Action > Upgrade Configuration Version.
Note : If the Upgrade Configuration Version option is grayed out or is not available, this means that your virtual machine is already at the highest supported configuration version.

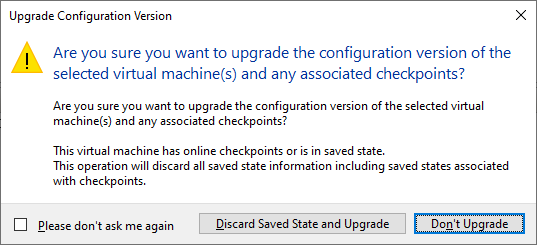
- A confirmation page will open asking you if you are sure you want to upgrade the configuration version for the selected virtual machine. If your virtual machine has associated checkpoints , the operation will discard all saved state information including saved stated associated with checkpoints. If you want cancel the upgrade click Don’t Upgrade, else to continue by clicking Discard Saved State and Upgrade

- The configuration version will be upgraded, as you can see in my setup, the configuration version for the selected virtual machine was 9.0 and now it is upgraded to 10.0 .
If you click on Action from the menu bar, you will see that Upgrade Configuration Version is no longer available as your virtual machine has the latest configuration version and no longer need an upgrade.

By diligently following these steps, you ensure that your virtual machine is running on an updated configuration version, unlocking new features and performance improvements. This becomes particularly crucial when utilizing the cluster OS rolling upgrade feature, as it aligns with the updated cluster functional level.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, maintaining an up-to-date virtual machine configuration version is paramount for compatibility and leveraging the latest Hyper-V features. By incorporating these simple steps into your routine, you not only enhance the efficiency of your virtual environment but also fortify its security and stability. Stay ahead in the virtualization game by embracing the power of upgraded configuration versions.
Related Article :How To Identify If Hyper-V Virtual Machine is Generation 1 Or Generation 2