Introduction:
Telnet is a simple text-based protocol that allows remote access to a server’s command-line interface. While Telnet is considered insecure and is not recommended for production environments, there may be situations where you need to enable the Telnet client for troubleshooting or specific requirements. In this tutorial, we’ll guide you through the process of enabling the Telnet client on Windows Server 2016, 2019, and 2022 using Server Manager.
To Enable Telnet in Windows Server, follow the below step:
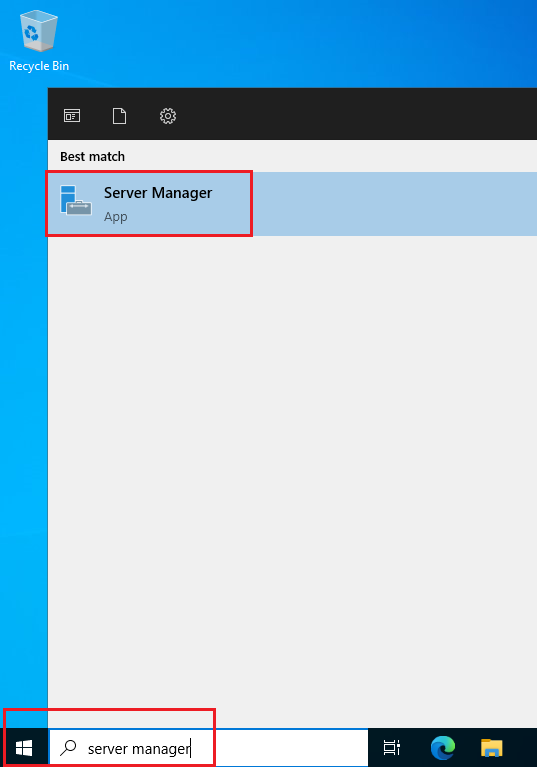
- Initiate the process by launching Server Manager. Click Start and then Server Manager

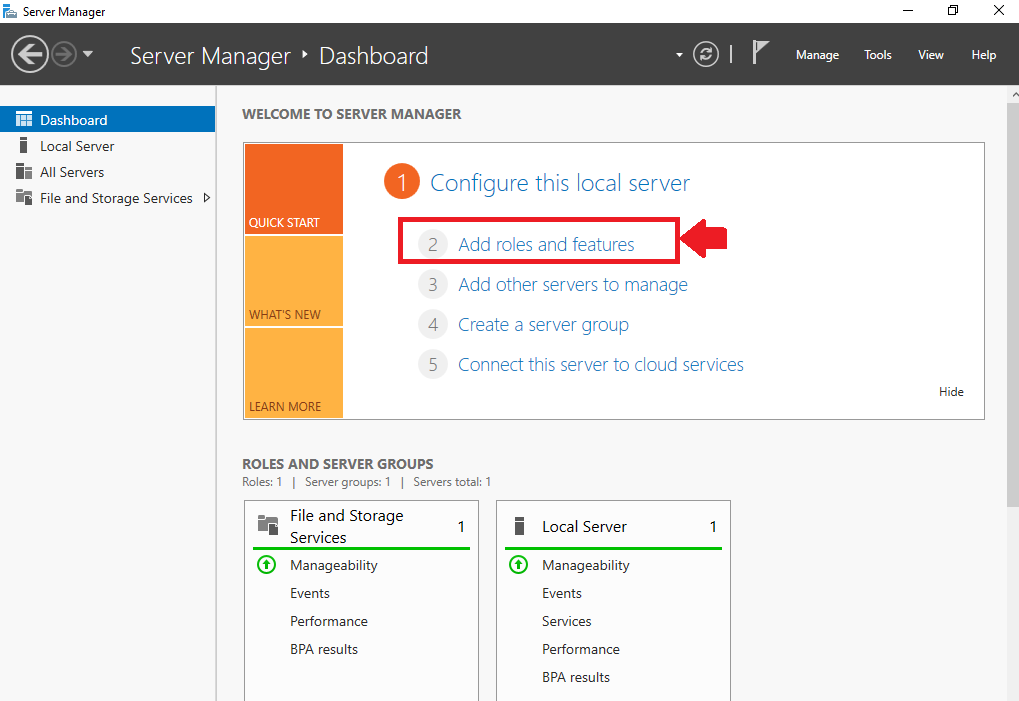
- Once Server Manager is open, Click Add Roles and Features. This action initiates the Add Roles and Features Wizard.

- In the Before you begin page, click Next

- In the Installation Type page, choose Role-based or feature-based installation and proceed by clicking Next.

- In the Server Selection page, ensure Select a server from the server pool is selected, then choose your server from the list. Click Next to continue.

- On the Server Roles page, we will not be selecting anything from here, so click Next

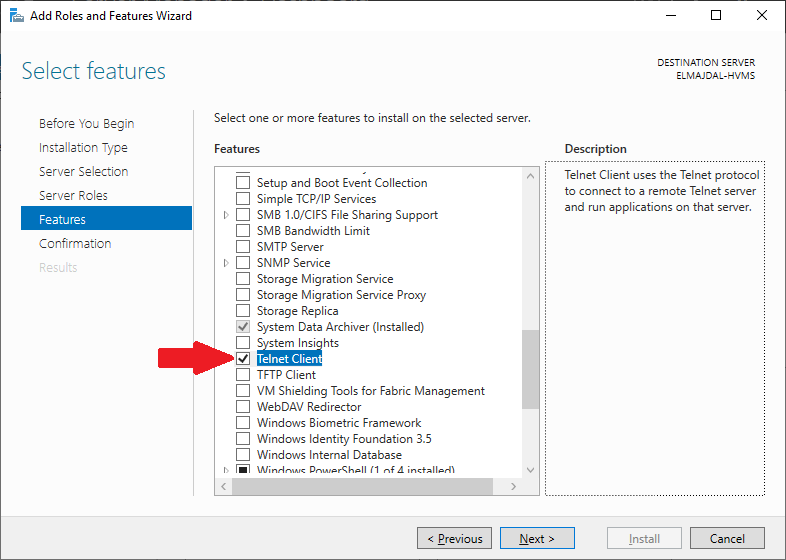
- On the Features page, scroll down till you see Telnet Client, select the checkbox beside it and click Next

- Review your selections, ensuring that Telnet Client is listed. Telnet Client does not require to restart the server once installation is completed, so no need to select the Restart the destination server automatically if required. Click Install

- Keep an eye on the installation progress displayed on the Results page. After the installation concludes, click on Close.

To Verify Telnet Client Installation
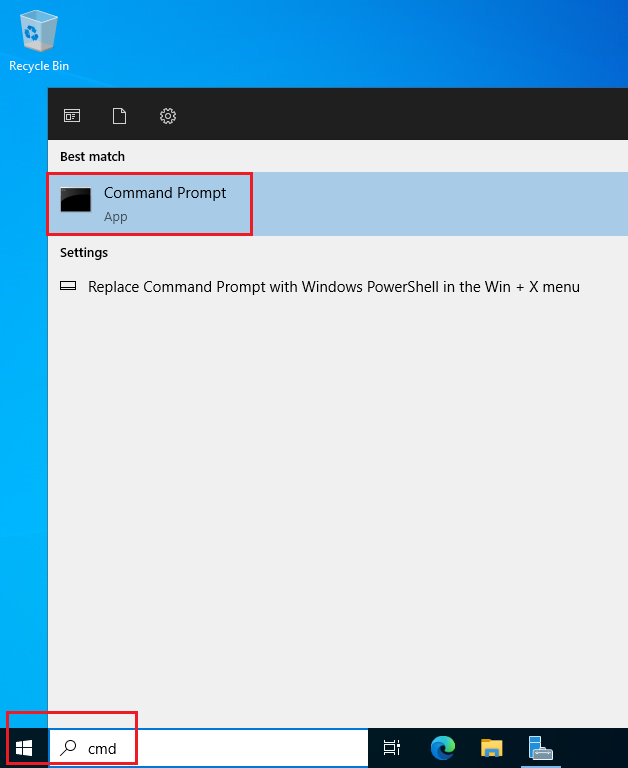
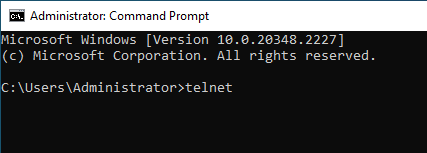
- Open a command prompt

- In the command prompt, type the telnet and click Enter

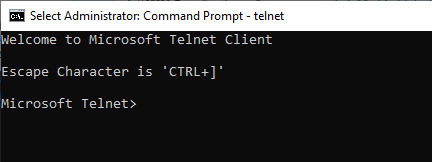
- If Telnet is installed, the command prompt will display the Telnet prompt, indicating a successful installation.

Congratulations! You have successfully enabled the Telnet Client on your Windows Server 2016, 2019, or 2022 using Server Manager. Keep in mind that while Telnet can be useful for specific tasks, it is generally recommended to use more secure alternatives, such as Secure Shell (SSH), for remote access to servers.