Introduction
The primary reason why SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is used is to keep sensitive information sent across the Internet encrypted so that only the intended recipient can understand it. This is important because the information you send on the Internet is passed from computer to computer to get to the destination server. Any computer in between you and the server can see your usernames and passwords, and other sensitive information if it is not encrypted with an SSL certificate. When an SSL certificate is used, the information becomes unreadable to everyone except for the server you are sending the information to. This protects it from hackers and identity thieves.
Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 creates a self-signed certificate during installation that uses all the server and domain names known to Exchange at the time of installation. The certificate name is Microsoft Exchange, and as you can see from the below snapshot, it is self signed.
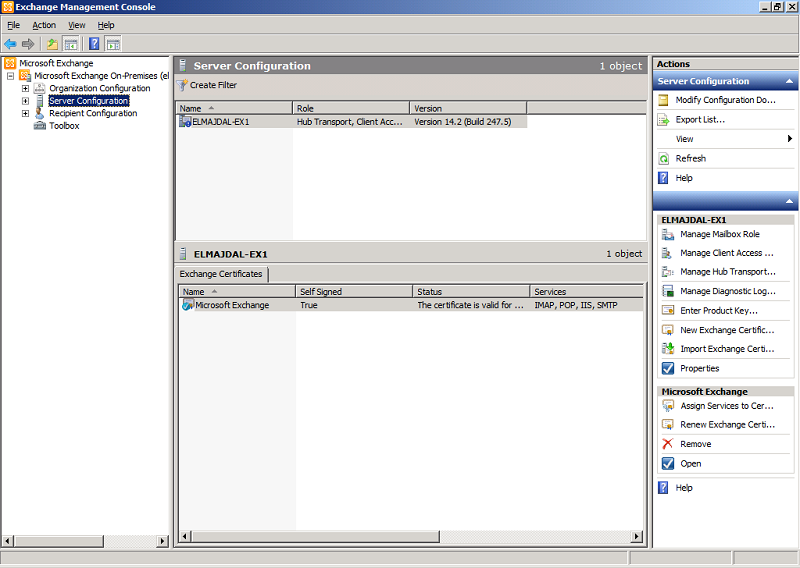
However, you can also use certificates signed by a certification authority (CA). If you are using a CA to generate certificates, you must provide a certificate request according to that CA’s requirements. You must contact your CA to determine its requirements for new certificate requests. After you have sent the certificate request to a CA, the CA issues a certificate .
There are many Certificate Authority providers that you can purchase your SSL certificate from. If you prefer to purchase from a Microsoft Partner, then Microsoft already lists some Unified Communications certificate partners, you can find them here http://support.microsoft.com/kb/929395
Installing an SSL Certificate in Exchange Server is done in these steps:
-
Buying an SSL certificate from a Certificate Authority
-
Producing a Certificate Request File
-
Use the Complete Pending Request wizard to map the certificate to the certificate request created on the server.
-
Assign the Exchange services to the certificate using the Assign Services to Certificate wizard.
So lets start with issuing a certificate request file, then we will produce our certificate from a Certificate Authority and map this certificate to the request file. Later on we will assign the required services to the certificate:
1. Open Exchange Management Console and from the left side pane, click on Server Configuration
 .
.
2. From the right side node, click on New Exchange Certificat
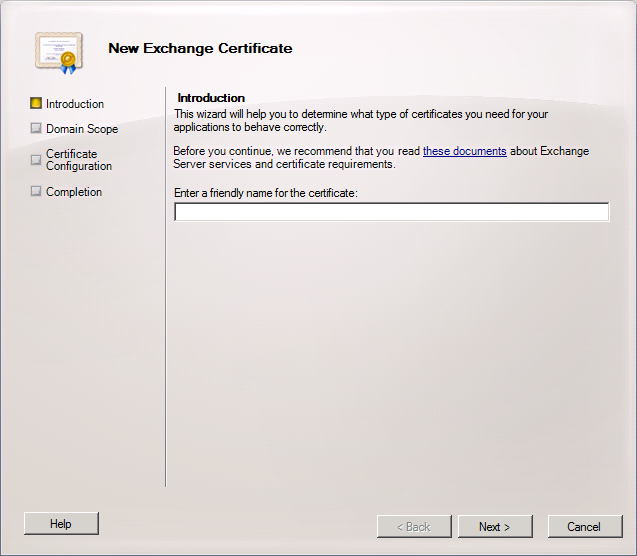
3. On the Introduction, type a friendly name for the certificate, I will have the friendly name as mail.elmajdal.com
Click Next
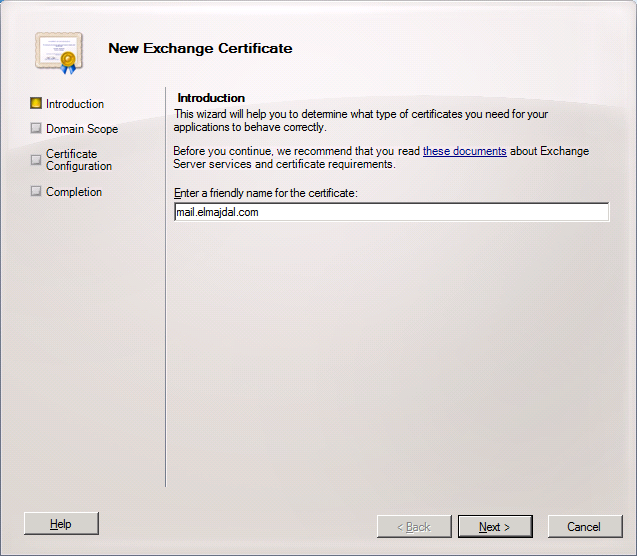
4. If you want to enable wildcard certificate, then enable the check box and type the root domain for wildcard. If you don’t have a wild card certificate, then skip this step and click Next .
I will skip this step, as I will buy and install a Unified Communications Certificate. Unified Communications Certificates (UCC) are SSL Certificates that secure multiple domains and multiple hostnames within a domain. UC Certificates are ideal for Microsoft Exchange Server 2007, Exchange Server 2010, and Microsoft Live Communications Server.
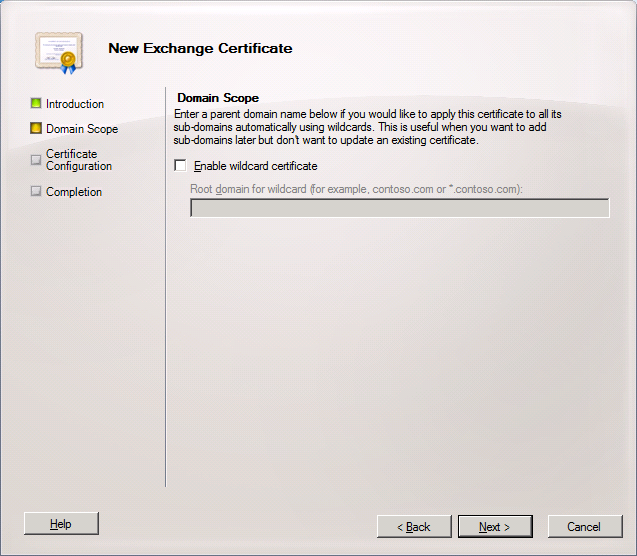
5. On the Exchange Configuration page, you will need to select the services and protocols that your certificate will need to support. Choose from the following options:
Federated Sharing If you will be using this certificate for Federated Sharing, select the Use this certificate for Federated Sharing check box.
Client Access server (Outlook Web App) If you’ll be using this certificate for Outlook Web App, select the appropriate boxes for Outlook Web App on the Intranet or on the Internet and enter the domain name you use to access Outlook Web App.
Client Access server (Exchange ActiveSync) If you’ll be using this certificate for Exchange ActiveSync, select the Exchange ActiveSync is enabled check box and enter the domain name you use to access Exchange ActiveSync.
Client Access server (Exchange Web Services, Outlook Anywhere, and Autodiscover) If you’ll be using this certificate for Exchange Web Services, Outlook Anywhere, or the Autodiscover service, select the applicable check boxes and enter the external host name for your organization. For the Autodiscover service, choose whether you will be using the Long URL format, the Short URL format, or a custom format. In the Autodiscover URL to use box, enter the full URL to the Autodiscover service.
Client Access server (POP/IMAP) Select the check boxes to specify whether your users will be using POP and IMAP on the Intranet and the Internet. Enter the domain names to use for both POP and IMAP.
Unified Messaging Server If you’ll be using Unified Messaging, choose whether you’ll use a self-signed certificate or a public certificate. You must use a public certificate if you are using Unified Messaging with Office Communications Server. For either option, enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of your Unified Messaging server.
Hub Transport Server Enter the FQDN of your Hub Transport server if you’ll be using mutual TLS to help secure Internet mail or if you’ll be using a Hub Transport server for POP and IMAP client submission.
Legacy Exchange Server Select Use legacy domains and enter the legacy domain name if you’re upgrading from a previous version of Exchange Server and will be operating in a coexistence scenario for a period of time during the upgrade.
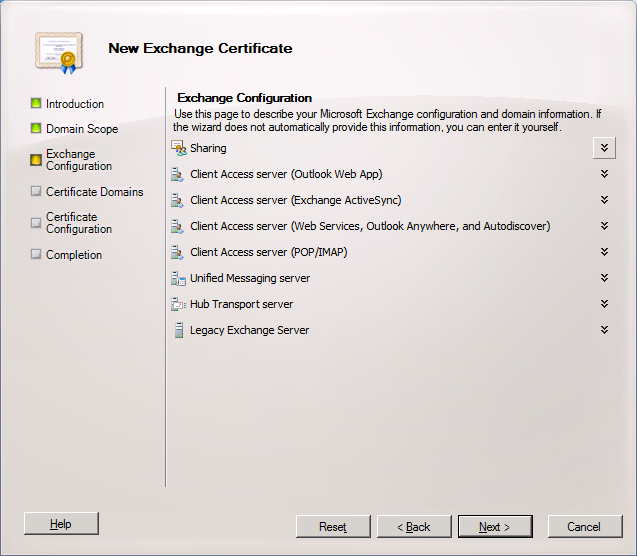
I will be only enabling OWA and Autodiscover.
Expand Client Access server (Outlook Web App) and select the checkboxes beside Outlook Web App is on the Intranet and Outlook Web App is on the Internet, as I will allow my users to access OWA from inside the LAN and from the Internet.
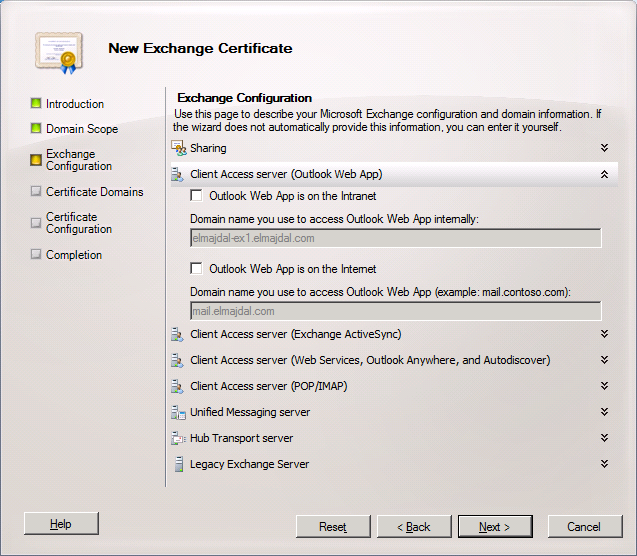
I will have both names refer to the same domain name : mail.elmajdal.com
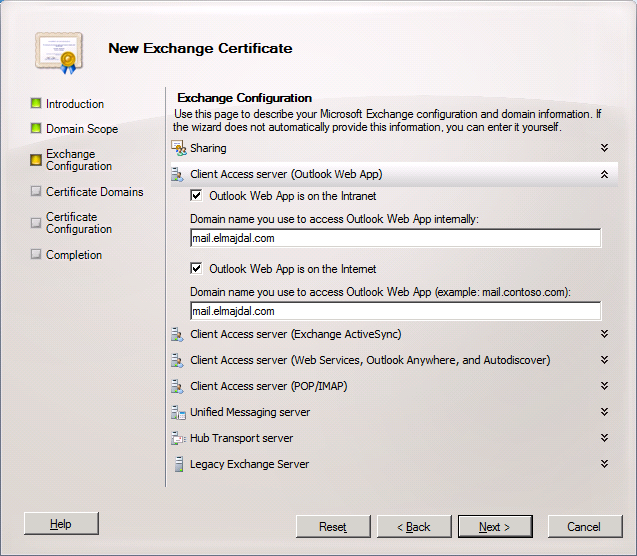
Then expand Client Access server (Web Services, Outlook Anywhere, and Autodiscover) and make sure all selected and the domain names are properly configured ( mail.elmajdal.com and for autodiscover : autodiscover.elmajdal.com)
Click Next to continue
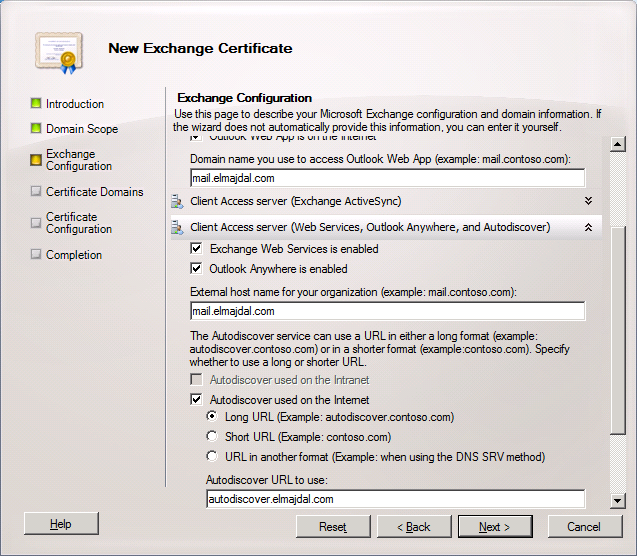
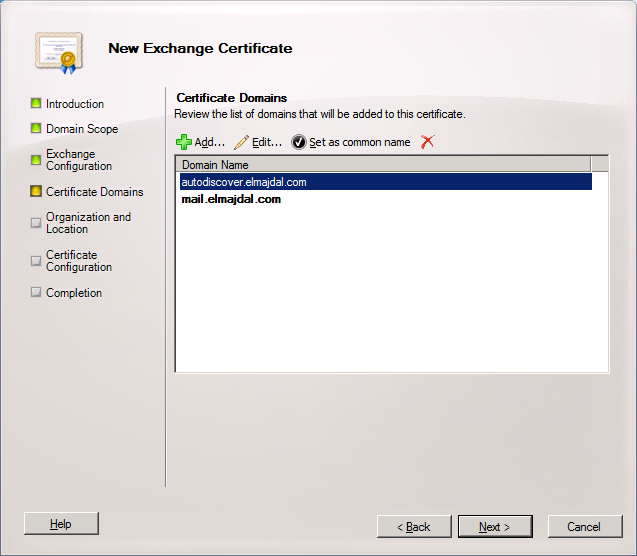
6. On the Certificate Domains page, review the list of domains that will be added to the certificate, the common name for the certificate will be displayed in bold. Click Next
7. On the Organization and Location page, fill all the fields with your organization information
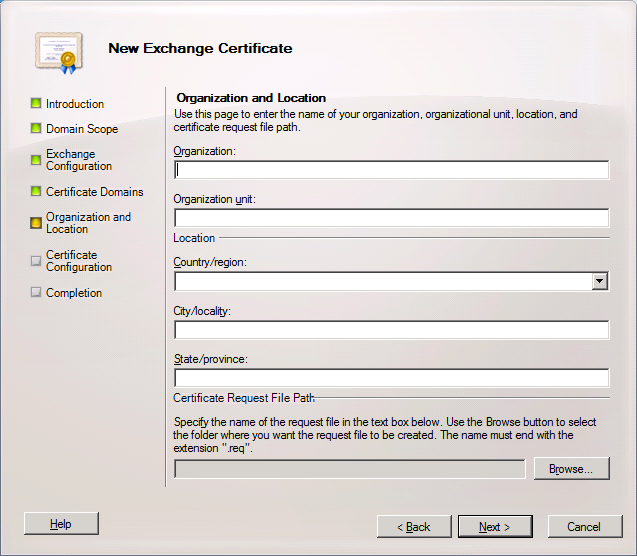
and then browse to the location where you want to save the Certificate Request file
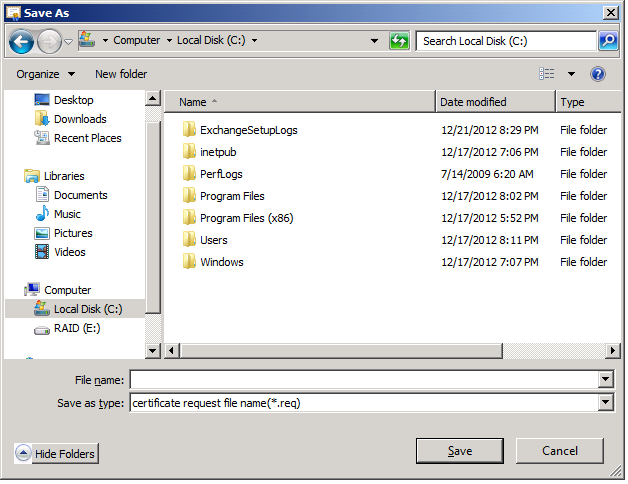
This how it should look like after all fields are filled. Click Next
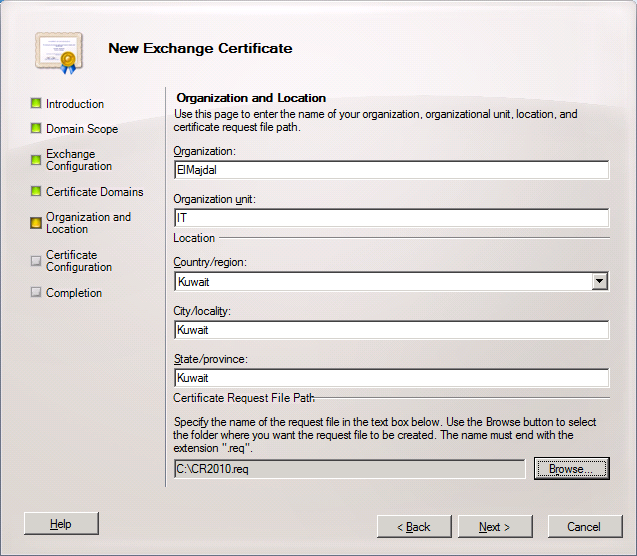
8. The last page before issuing the Certificate Request file is the Certificate Configuration page, where you can review your data entered . If you need to make any changes, click Back and change the required configuration, else Click New to complete the process
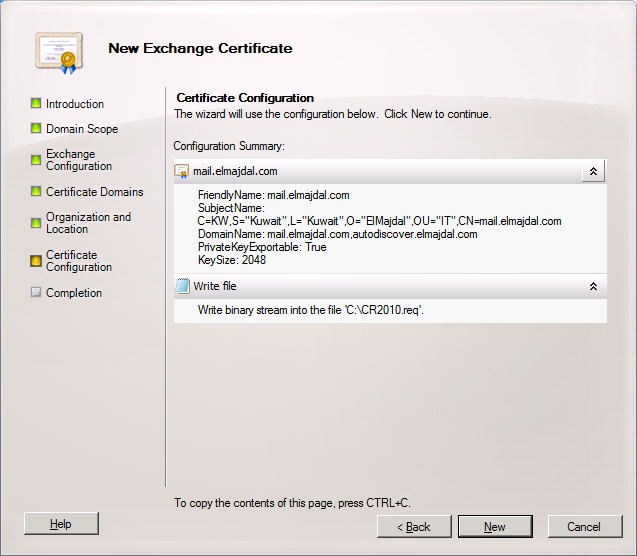
9. The wizard will complete successfully. Click Finish to close the wizard.
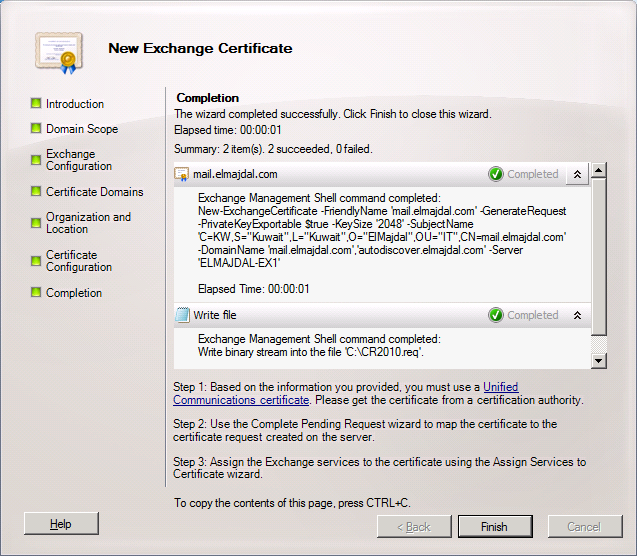
In Exchange Server, now we will be having a certificate with a status of pending . What is needed now is to open the certificate request file that was exported in the previous steps, copy its content and paste it inside the Certificate Authority
Go to the location where you saved the certificate request file and open it. The file can be opened with notepad.
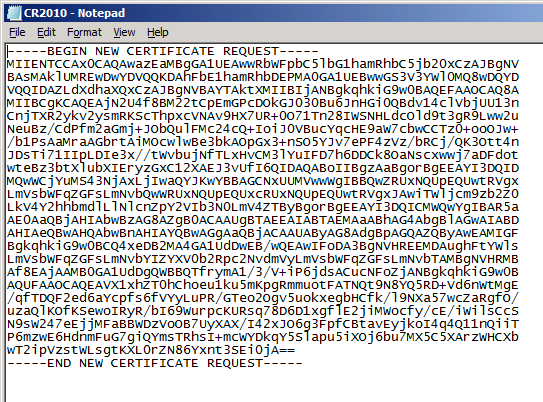
This is how the certificate request file looks like, it begins with —-BEGIN NEW CERTIFICATE REQUEST—– and ends with —–END NEW CERTIFICATE REQUEST—–
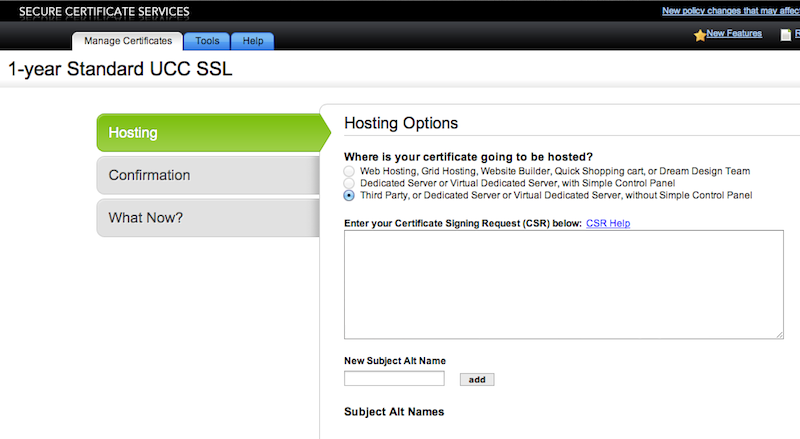
Now copy the complete content of the certificate request file, and go to your certificate authority website, where you have bought a Unified Communications Certificate, Paste the content of the Certificate Request file, into the specified text area on the CA website. Your Certificate files will be generated and you will be able then to download it.
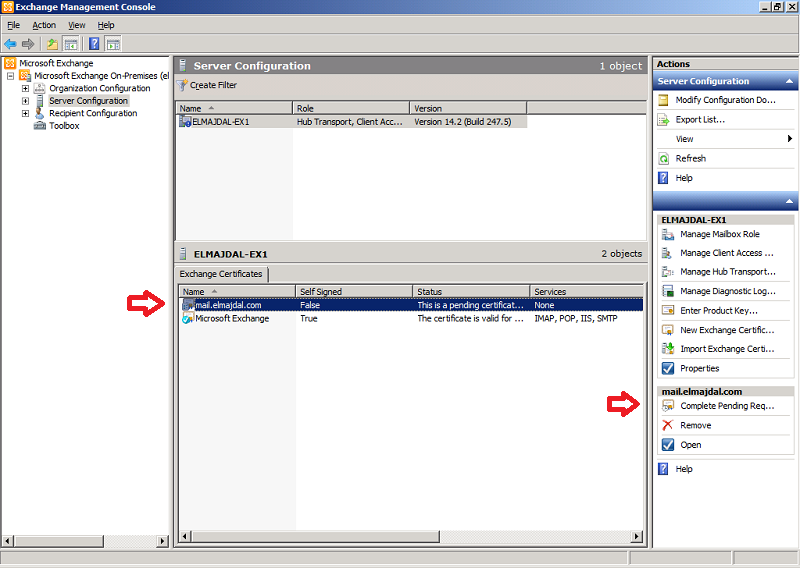
11. Now back to Exchange console, select the pending certificate and then from the right side pane, click on Complete Pending Request
This wizard walks you through the steps needed to complete the request and import the new certificate to your Exchange server. Before the import occurs, the certificate will be mapped to the certificate request that already exists on the server.
12. On the Introduction page of the Complete Pending Request wizard, click Browse and select the certificate that was issued and downloaded from the Certificate Authority. This will map the certificate to the certificate request.
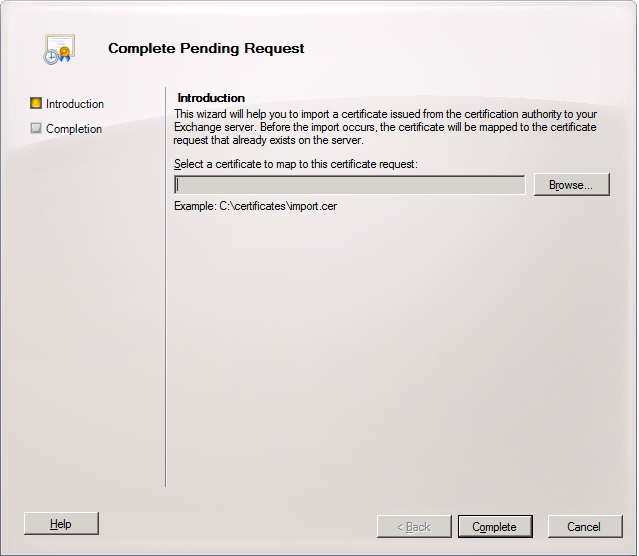
From the file type, select Base-64 encoded X.509 (*cert) and the certificate will be displayed
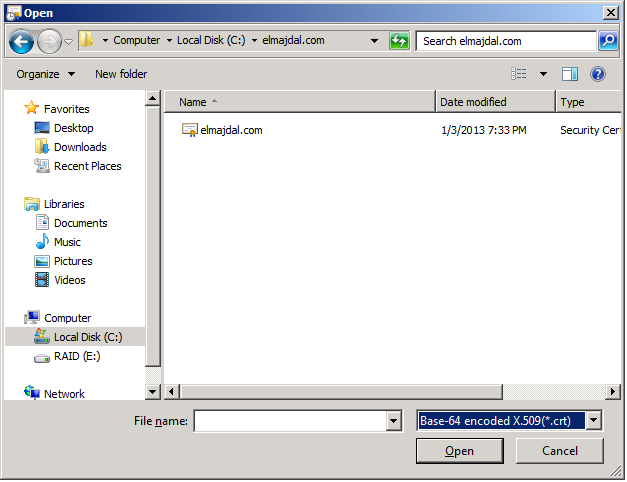
Once the certificate is selected, click Complete
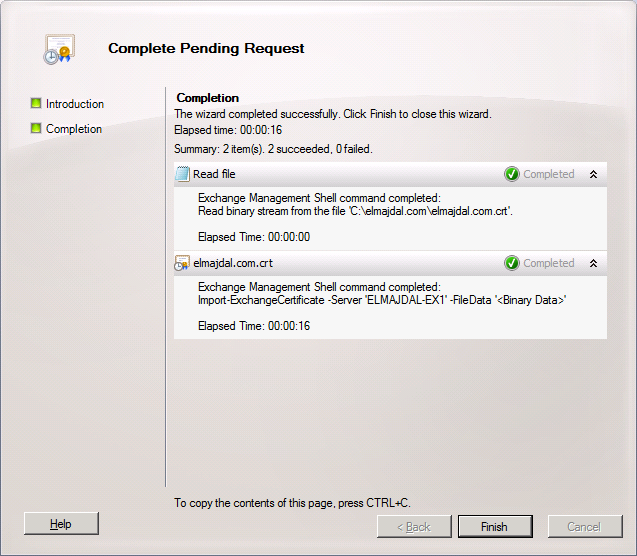
13. The wizard will complete successfully, click Finish
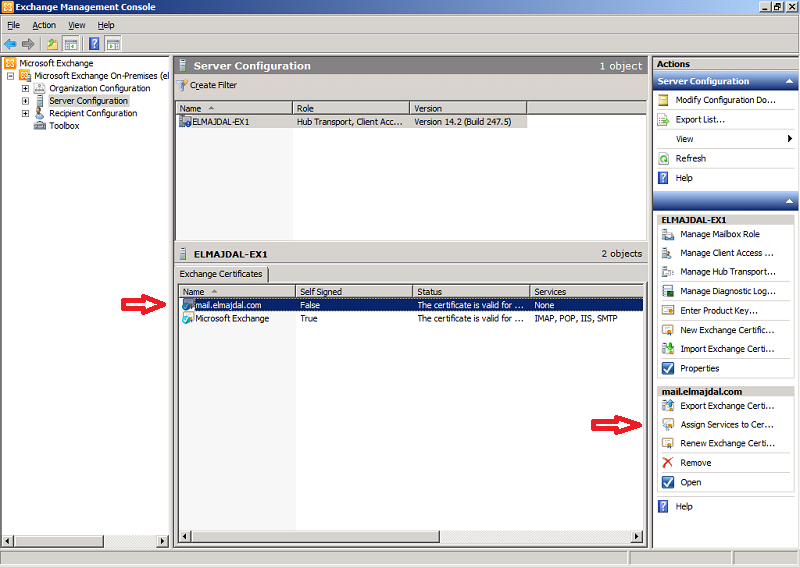
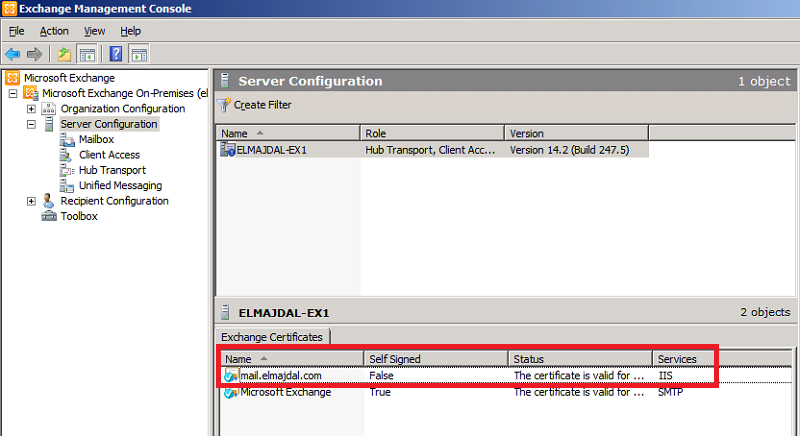
14. The Certificate status will be changed from Pending to Valid. One last step is to configured this certificate with the appropriate services. As you can see now, there is no services configured with this certificate and the column for the Services shows None.
To complete this step , select the certificate and from the right side pane, click Assign Services to Certificate…
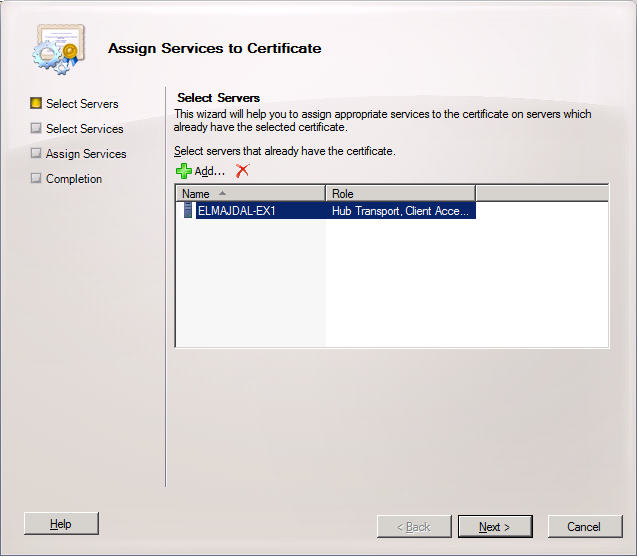
15. On the Select Servers page, select the server that has the certificate and want to assign the required services
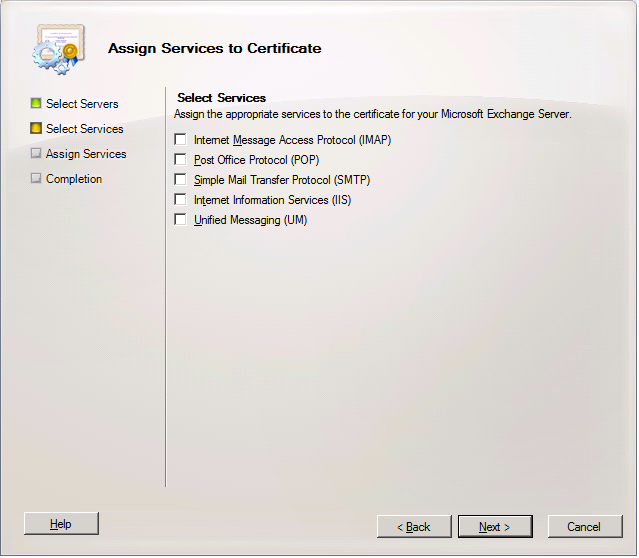
16. On the Select Services page, use the check boxes to choose the services you want to assign to your certificate.
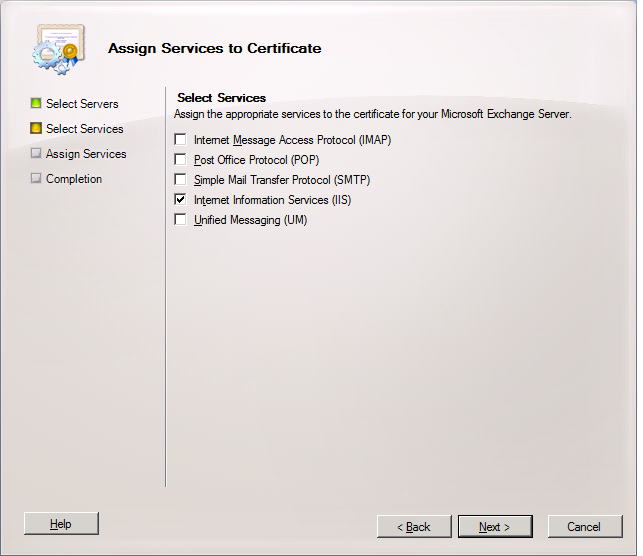
For example, for OWA and Exchange Anywhere, you can select Internet Information Services.
When you select the required services, click Next
Note : If you attempt to assign the Unified Messaging service to the certificate and the certificate is running in TCP mode only, assignment will fail. In order to use a certificate for Unified Messaging, it must be set to run in TLS mode or Dual mode.
17. The configuration page is simple. Its showing the services you selected under the selected server. Click Assign
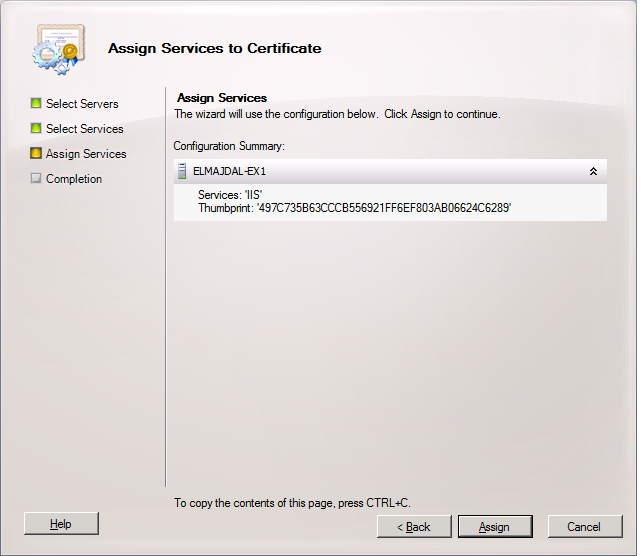
18. The wizard will be successfully completed, click Finish
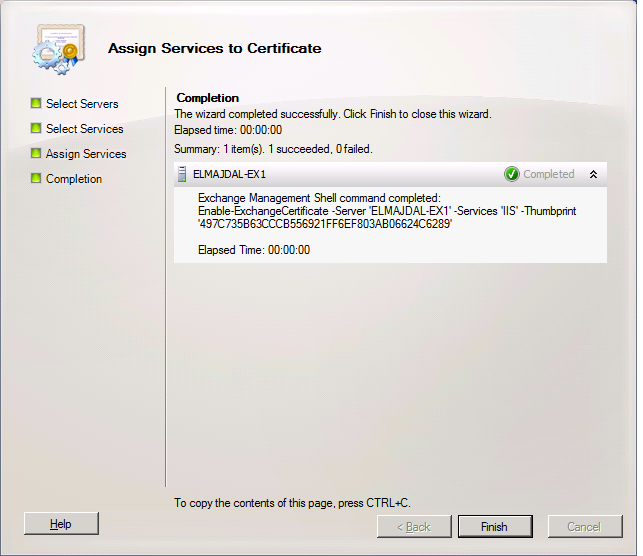
19. That is all. You have successfully issued a certificate request, mapped a certificate to that certificate request and finally assigned the required services for this certificate.
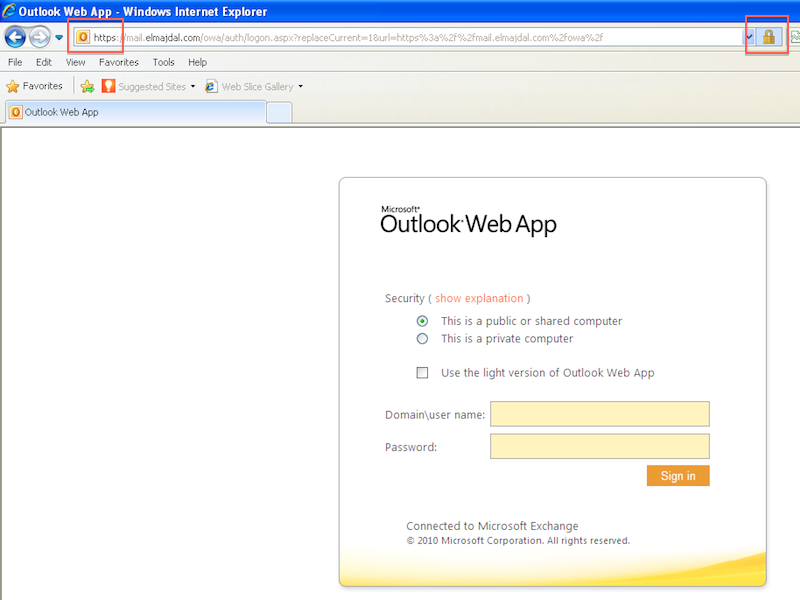
20. Now to test the SSL certificate, open an internet browser, and go to : https://mail.elmajdal.com/owa
You will notice that the website will load with a valid certificate.